Z Transform Transfer Function Block Diagram 31++ Images Result
Z Transform Transfer Function Block Diagram. For clarity, we present the corresponding formula for the siso system. 1;1;2;3;5;8;13 ;21 ;34 ;55 ;:::
The transfer function for the linearized system from It consists of unidirectional, operational blocks that represent the transfer function of the variables of interests. Repeat steps 1 to 3 for each of the remaining inputs.
vauxhall zafira fuse box diagram 2000 daihatsu charade g30 wiring diagram fuse box 1999 subaru forester saturn sl2 stereo wiring diagram
PPT z Transform Signal and System Analysis PowerPoint
Let the transfer function be ˆg[z] = β1zn−1 +β2zn−2 +···+βn zn +α1zn−1 +α2zn−2 +···+αn +γ Or you can use z transform as above which gives a more compact solution. Calculate the response due to the chosen input acting alone. Each step refers to specific transformations listed in fig.

Source: slideserve.com
Combine all cascade blocks using transformation 1. 4.1 block diagrams 4 system xfer functions 4.1 block diagrams yn +0:2yn. H(z)=h1(z)+h2(z) serial or cascade system: A transfer function, g (s), relates an input, u (s), to an output, y (s). C) draw the form ii block diagram for this iir filter.

Source: chegg.com
Fya 112+2} d d 3 b) = a system is specified by its z transfer function z + 1 g (2) z2 + 0.5z + 0.12 what is the order n of the system? Step 2 combine all parallel blocks using transformation 2. Transfer functions the transfer function of a linear system is the ratio of we need ways to.

Source: slideserve.com
Repeat steps 1 to 3 for each of the remaining inputs. For any proper transfer matrix it is also possible to construct a corresponding canonical state space equation. Fir and iir filters, and system functions 2 the system function and block diagrams 3 inverse z transform 4 summary )draw the form i block diagram for this iir filter. C) draw.
![[MW_0767] Block Diagram Z Transform Free Diagram [MW_0767] Block Diagram Z Transform Free Diagram](https://i2.wp.com/static-assets.imageservice.cloud/10215365/transfer-function-stability-criteria-of-type-3-digital-pll.png)
Source: frag.venet.mohammedshrine.org
For the integrals that are in the diagram, we must consider laplace because the laplace transform of the integrals in our diagram are equal to $\frac{1}{s}$, replace in the diagram: It consists of unidirectional, operational blocks that represent the transfer function of the variables of interests. The transfer function for the linearized system from Yx x y zzzzzz = −.
![[MW_0767] Block Diagram Z Transform Free Diagram [MW_0767] Block Diagram Z Transform Free Diagram](https://i2.wp.com/static-resources.imageservice.cloud/16749860/mm3fc-mathematical-modeling-3-lecture-6-times-weeks-78-9.jpg)
Source: frag.venet.mohammedshrine.org
4.1 block diagrams 4 system xfer functions 4.1 block diagrams yn +0:2yn. For the integrals that are in the diagram, we must consider laplace because the laplace transform of the integrals in our diagram are equal to $\frac{1}{s}$, replace in the diagram: Y x = h (r ) = 1 1 rr. Yx x y zzzzzz = − − −−.

Source: chegg.com
H(z)=h1(z)+h2(z) serial or cascade system: Step 2 combine all parallel blocks using transformation 2. I and my friend have different answer for this block diagram mine: Y x = h (r ) = 1 1 rr. Calculate the response due to the chosen input acting alone.
![[MW_0767] Block Diagram Z Transform Free Diagram [MW_0767] Block Diagram Z Transform Free Diagram](https://i2.wp.com/static-resources.imageservice.cloud/10215345/z-transform-transfer-function-block-diagram-wiring-diagram-schematic.jpg)
Source: frag.venet.mohammedshrine.org
Let the transfer function be ˆg[z] = β1zn−1 +β2zn−2 +···+βn zn +α1zn−1 +α2zn−2 +···+αn +γ A transfer function, g (s), relates an input, u (s), to an output, y (s). There are a lot of choices for you to convert block diagram to transfer function that you can find at convert2f.net. It consists of unidirectional, operational blocks that represent the.
![[MW_0767] Block Diagram Z Transform Free Diagram [MW_0767] Block Diagram Z Transform Free Diagram](https://i2.wp.com/static-assets.imageservice.cloud/10215347/z-transform-transfer-function-block-diagram-just-wiring-diagram.jpg)
Source: frag.venet.mohammedshrine.org
The first step in creating a transfer function is to convert each term of a differential equation with a laplace transform as shown in the table of laplace transforms. Y [n ] = x [n ]+ y [n 1]+ y [n 2] h (z) = y (z) x (z) = z. You can freely choose the most. Eliminate all minor.

Source: chegg.com
Each step refers to specific transformations listed in fig. You can freely choose the most. Transfer function is gˆ 1[z]+gˆ2[z] = c(zi − a)−1b +d. C) draw the form ii block diagram for this iir filter. Y [n ] = x [n ]+ y [n 1]+ y [n 2] h (z) = y (z) x (z) = z.

Source: chegg.com
The first step in creating a transfer function is to convert each term of a differential equation with a laplace transform as shown in the table of laplace transforms. )draw the form i block diagram for this iir filter. For clarity, we present the corresponding formula for the siso system. Fir and iir filters, and system functions 2 the system.

Source: slideshare.net
Transfer function is defined as the relationship between an input signal and an output signal to a device. Yx x y zzzzzz = − − −− 2 1 2 11 h. Set all inputs except one equal to zero. Step 2 combine all parallel blocks using transformation 2. H(z)=h1(z)+h2(z) serial or cascade system:

Source: slideserve.com
Calculate the response due to the chosen input acting alone. Find the z transfer function from the following block diagram realization of the system in time domain. Or you can use z transform as above which gives a more compact solution. Y x = h (r ) = 1 1 rr. For any proper transfer matrix it is also possible.

Source: chegg.com
Repeat steps 1 to 3 for each of the remaining inputs. For the integrals that are in the diagram, we must consider laplace because the laplace transform of the integrals in our diagram are equal to $\frac{1}{s}$, replace in the diagram: A block diagram can be used simply to represent the composition and interconnection of a system. The first step.
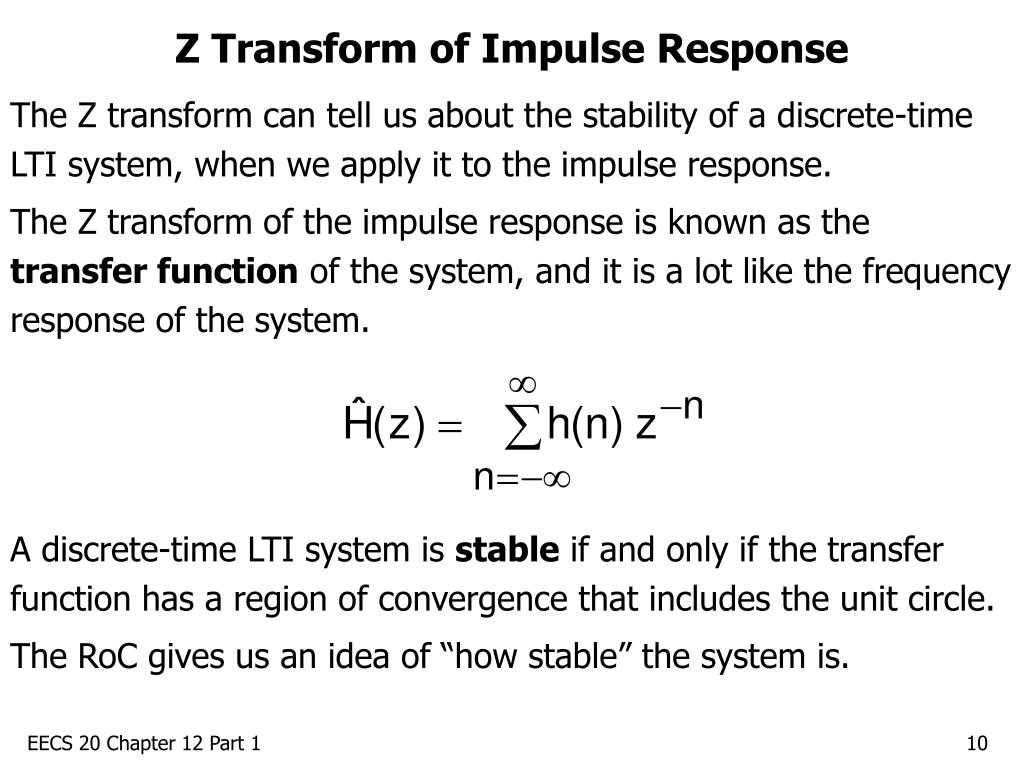
Source: slideserve.com
The following general steps may be used as a basic approach in the reduction of complicated block diagrams. There are a lot of choices for you to convert block diagram to transfer function that you can find at convert2f.net. For clarity, we present the corresponding formula for the siso system. Transfer functions the transfer function of a linear system is.

Source: youtube.com
The first step in creating a transfer function is to convert each term of a differential equation with a laplace transform as shown in the table of laplace transforms. Y [n ] = x [n ]+ y [n 1]+ y [n 2] h (z) = y (z) x (z) = z. Suppose y(z) is the output, u(z) is the input,.
![[MW_0767] Block Diagram Z Transform Free Diagram [MW_0767] Block Diagram Z Transform Free Diagram](https://i2.wp.com/static-assets.imageservice.cloud/16749882/negative-feedback-loop-involving-two-cascaded-simple-regulations.png)
Source: frag.venet.mohammedshrine.org
For clarity, we present the corresponding formula for the siso system. Calculate the response due to the chosen input acting alone. G(s) = y (s) u (s) g ( s) = y ( s) u ( s) do the following, assuming that q and v are constant: A transfer function, g (s), relates an input, u (s), to an output,.

Source: ag67764.blogspot.com
Repeat steps 1 to 3 for each of the remaining inputs. Replace t [ n] and t [ n − 1] in (*) y [ n − 1] + y [ n − 2] = − y [ n − 1] + y [ n − 3] − x [ n − 1] + x [ n − 2] 2.

Source: studocu.com
Multiple representations of dt systems. Calculate the response due to the chosen input acting alone. Eliminate all minor feedback loops using transformation 4. Repeat steps 1 to 3 for each of the remaining inputs. Or you can use z transform as above which gives a more compact solution.
![[MW_0767] Block Diagram Z Transform Free Diagram [MW_0767] Block Diagram Z Transform Free Diagram](https://i2.wp.com/static-assets.imageservice.cloud/10215348/recurrence-relations-difference-equation-lti-system-z-transform.png)
Source: frag.venet.mohammedshrine.org
G(s) = y (s) u (s) g ( s) = y ( s) u ( s) do the following, assuming that q and v are constant: 4.1 block diagrams 4 system xfer functions 4.1 block diagrams yn +0:2yn. Find the z transfer function from the following block diagram realization of the system in time domain. About press copyright contact us.

Source: slideserve.com
For the integrals that are in the diagram, we must consider laplace because the laplace transform of the integrals in our diagram are equal to $\frac{1}{s}$, replace in the diagram: 4.1 block diagrams 4 system xfer functions 4.1 block diagrams yn +0:2yn. Repeat steps 1 to 3 for each of the remaining inputs. Let the transfer function be ˆg[z] =.